Understanding Facade Installation
What is Facade Installation?
Facade installation refers to the procedure of attaching the outer skin or covering of a building, which is not only aesthetic but also essential for structural, environmental, and functional purposes. A facade can be composed of various materials, including glass, metal, brick, stone, and composite materials. This process is crucial, as it affects the overall energy efficiency, durability, and visual appeal of a building. For a comprehensive guide on facade installation, you may refer to Facade Installation.
The Importance of Facades in Architecture
Facades are much more than mere protective barriers; they serve multiple purposes that are vital in modern architecture. A well-designed facade enhances a building’s aesthetic appeal, contributing to its identity and making it stand out within its surroundings. Additionally, facades play a significant role in energy efficiency by regulating heat and light intake, which can reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling systems.
Moreover, facades can improve indoor comfort by minimizing glare and achieving acoustic insulation, thus promoting a healthy living and working environment. The facade also acts as the first line of defense against environmental factors, protecting the structural integrity of the building from elements like wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations.
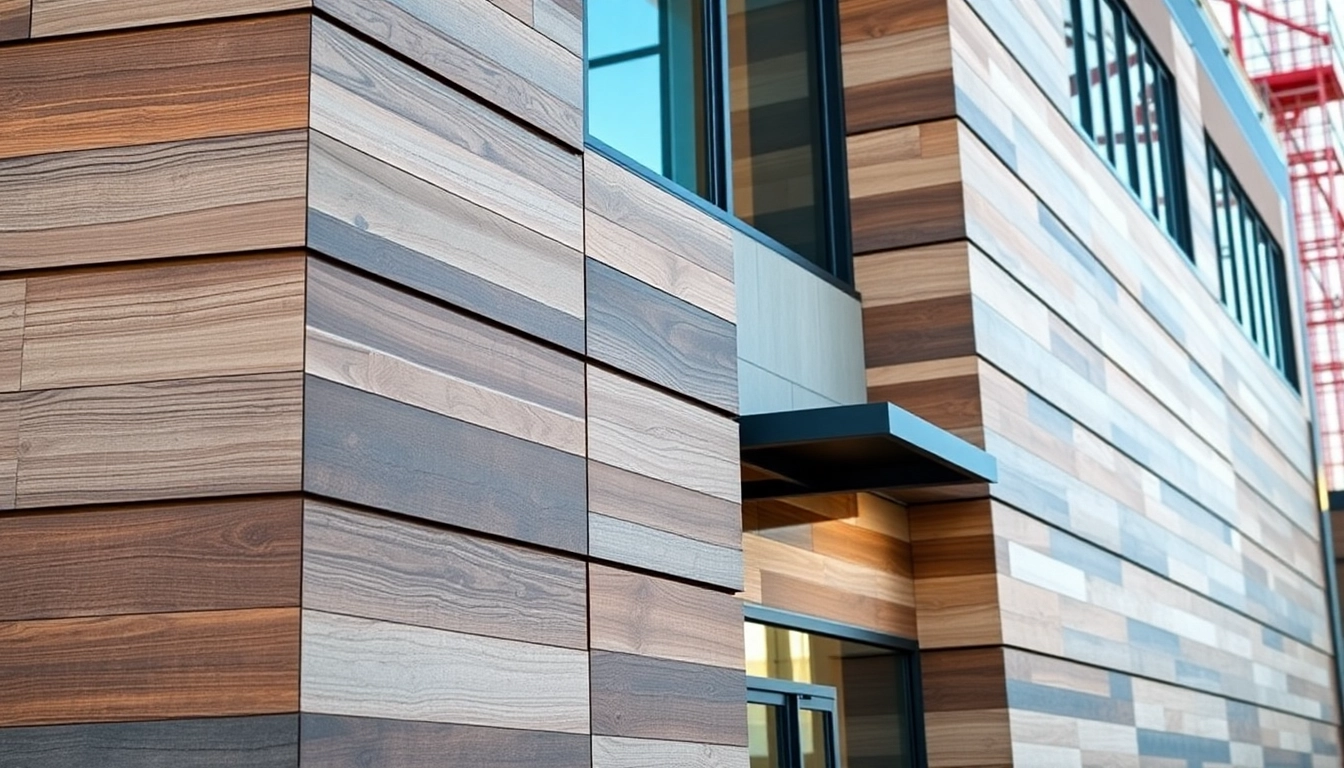
Common Materials Used in Facade Systems
The materials chosen for facade installation significantly impact the building’s performance and aesthetic quality. Common materials include:
- Glass: Renowned for its sleek appearance and ability to create a bright indoor environment, glass facades come in various types, including laminated, insulated, and frangible glass.
- Brick: Traditionally used for its durability and thermal properties, brick facades offer timeless appeal and can be combined with modern materials for versatility.
- Metal: Frequently employed for contemporary designs, metals such as aluminum and steel are lightweight, durable, and can be easily shaped into various forms.
- Stone: Offering unparalleled strength and natural aesthetics, stone façades are often used in high-end constructions.
- Wood: Adding warmth and character, wood facades are popular in eco-friendly designs but require regular maintenance to protect against the elements.
Preparation for Facade Installation
Assessing Site Conditions
The initial phase of facade installation requires an essential assessment of site conditions. This involves evaluating the geographical area, existing structures, and the ground’s load-bearing capacity. Additionally, understanding local climate conditions, including wind loads, snow loads, and rainfall patterns, is crucial for selecting appropriate materials and design.
Site surveys, including topographic mapping and soil testing, allow for the recognition of potential obstacles and hazards that may affect the installation process. This preparation stage is pivotal in ensuring safety and compliance with local building codes and regulations.
Choosing the Right Materials and Tools
Selecting suitable materials and tools for facade installation directly impacts the efficiency and quality of the work. Factors such as durability, weather resistance, and compatibility with existing structures should guide material selection. For instance, when choosing insulation materials, consider their R-value and fire resistance for optimal performance.
Tools play a crucial role as well; having the right tools, whether scaffolding, lasers for alignment, or adhesive applicators, ensures precision and expediency. Investing in quality equipment enhances the overall installation process, reducing delays and increasing safety.
Creating an Effective Installation Plan
A well-structured installation plan is critical to a successful facade project. This plan should outline specific goals, timelines, and workflows, incorporating contingencies for potential delays or issues. Mapping out each installation stage—from structural support to final touch-ups—helps streamline processes and allocate resources effectively.
Moreover, collaboration with architects, engineers, and contractors during the planning phase fosters communication and minimizes misunderstandings throughout the project life cycle.
Step-by-Step Facade Installation Process
Initial Setup and Structure Mounting
The initial setup involves strategically placing scaffolding to ensure worker safety and accessibility to high wall areas. Properly securing and aligning the structural framework is essential, as it will serve as a strong support system for the facade materials. Typically, facade systems are anchored to the building’s structural frame using mechanical fasteners, adhesives, or a combination of both, depending on the design and materials used.
This phase often includes installing a moisture barrier or insulation layer to prevent water ingress and regulate thermal performance, contributing to the building’s energy efficiency.
Applying Insulation and Weatherproofing
Once the structural framework is in place, applying insulation and weatherproofing is critical. Insulation types must be selected based on climate control goals, considering R-values and environmental impact. Common insulation materials include rigid foam boards, spray foam, or fiberglass batts.
After installation of the insulation, a weather-resistant barrier protects the structure from external moisture. This element acts as a safeguard, preventing water damage and contributing to the building’s longevity. Ensuring the overlap and fastening of this barrier is done correctly is vital to maintain the integrity of the entire facade system.
Final Cladding Techniques and Finishing Touches
The final cladding techniques vary based on the selected facade materials. For example, when installing glass panels, precise measurements and careful handling are necessary to avoid breakage. For brick or stone façades, a consistent mortar mix and correct layering techniques ensure stability and uniform appearance.
Finishing touches, such as applying sealants and weather stripping around joints and edges, enhance the facade system’s performance, protecting against air and moisture infiltration. Performing quality checks throughout this phase guarantees that all systems function as intended and meet architectural specifications.
Challenges in Facade Installation
High-Rise Installation Issues
Installing facades on high-rise buildings presents unique challenges. The height often requires specialized equipment like cranes, lifts, and scaffolding that can safely accommodate personnel and materials.
Additionally, extreme weather conditions at elevated heights can complicate installation schedules. Therefore, planning installation timing and methods with the potential for wind load and precipitation is crucial.
Weather and Environmental Factors
Weather plays a critical role in facade installation. Rain, snow, or excessive heat during installation can impact the curing processes of adhesives and mortar, compromising the quality of the facade. As such, implementing weather forecasts into the planning stages becomes essential in minimizing interruptions and ensuring consistent work quality.
Material Compatibility Challenges
Compatibility issues can arise when different materials are combined, affecting the overall performance and aesthetic of the facade. Factors such as thermal expansion and contraction, porosity, and adhesion strength contribute to these challenges.
Conducting thorough material testing and consulting with manufacturers can help identify potential issues and develop solutions to ensure that all materials perform harmoniously together.
Best Practices for Efficient Facade Installation
Quality Control and Safety Management
Implementing stringent quality control measures throughout the facade installation process is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness. Regular inspections and compliance checks help maintain standards that prevent costly reworks and contribute to overall safety on-site.
Establishing clear safety protocols, providing training for workers, and ensuring the availability of safety equipment reduce the risk of accidents and injury, fostering a safer working environment.
Innovative Technologies in Facade Design
Emerging technologies in facade design and materials are changing the landscape of facade installation. Innovations such as prefabricated panels, modular systems, and advanced building information modeling (BIM) facilitate easier assembly and higher precision in installation.
Utilizing energy-efficient materials with built-in thermal performance boosts sustainability, while smart facades equipped with sensor technologies can actively respond to environmental conditions, enhancing user comfort and energy management.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Maintenance is a crucial component in enhancing the longevity of facade systems. Regular inspections allow for the early identification of wear or damage, permitting timely repairs that can prevent larger issues down the line. It is essential to check for loose panels, cracked joints, and signs of age in materials.
Cleaning facades periodically not only maintains their aesthetic appeal but also ensures the materials function efficiently by removing debris that could lead to moisture retention. Additionally, applying protective coatings can significantly enhance a facade’s resilience against UV exposure and environmental damage.