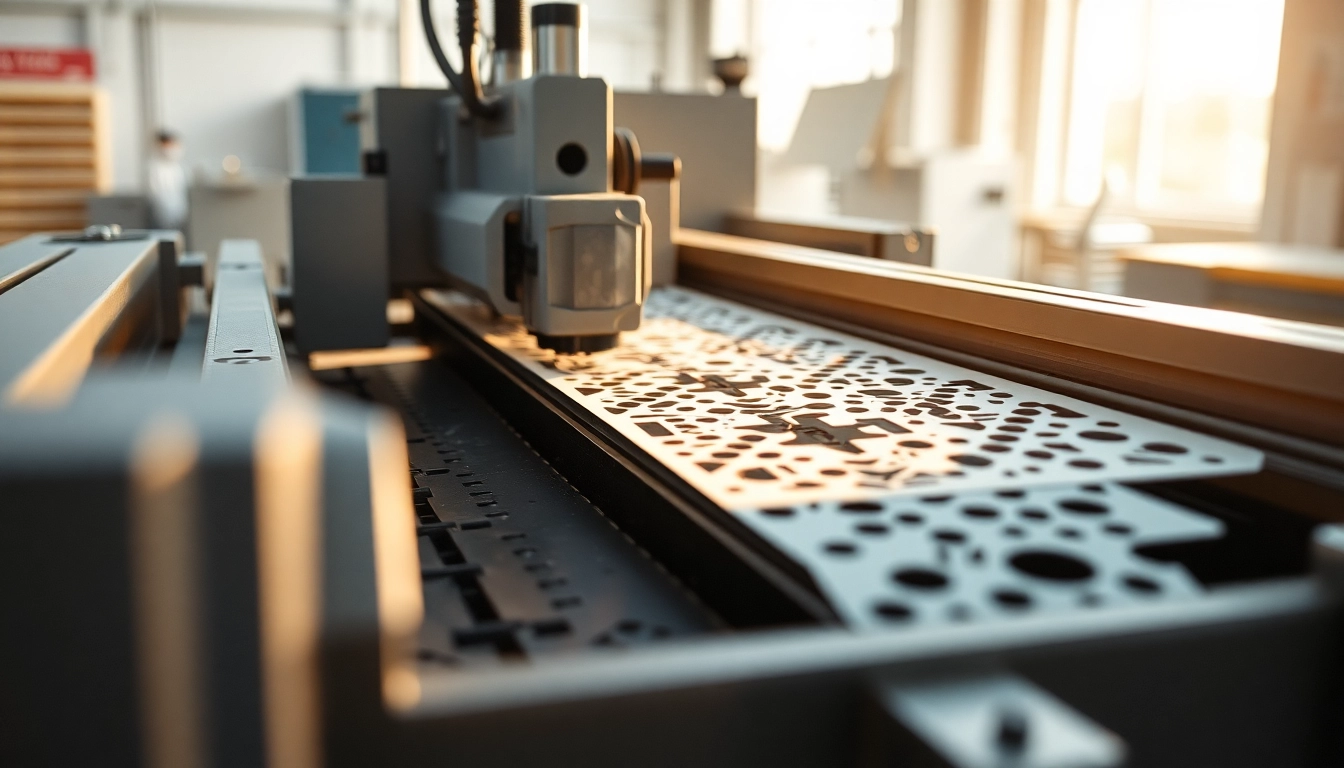
Understanding Precision Die Cutting
Precision die cutting is a fundamental process in the manufacturing sector, offering the ability to produce intricate shapes and designs with unparalleled accuracy. By utilizing specialized techniques, manufacturers can convert flat materials into custom shapes, making it a vital service in various industries, including packaging, automotive, medical, and electronics. Through methods such as flatbed and rotary die cutting, businesses can achieve high-volume production while ensuring minimal waste and maintaining tight tolerances, often as low as +/− 0.005 inches. For an in-depth exploration of this sophisticated process, refer to our page on precision die cutting.
What is Precision Die Cutting?
At its core, precision die cutting is a manufacturing process that uses a die to cut specific shapes out of a wide variety of materials, including paper, plastic, rubber, and foam. The die is crafted to match the specific shapes required for a project, allowing for consistent and repeatable cuts. Unlike traditional cutting methods, die cutting aids in producing complex designs and high-quality results at scale. This process can be broadly categorized into two main types: flatbed die cutting and rotary die cutting.
Key Technologies in Die Cutting
Modern die cutting processes leverage advanced technologies that enhance precision and efficiency:
- Flatbed Die Cutting: This traditional method employs a flat surface on which the material is placed, and a hydraulic press moves down to cut through it. This technique is well-suited for intricate designs and multiple layers.
- Rotary Die Cutting: Utilizing cylindrical dies, this method allows for continuous cutting and is typically faster than flatbed cutting. It is ideal for producing high volumes of parts, especially in the packaging industry.
- Laser Die Cutting: An alternative to mechanical die cutting, laser cutting offers exceptional precision and flexibility, able to cut complex patterns without the need for physical dies. This technology is particularly beneficial for prototyping and low-volume production runs.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of precision die cutting allows it to be applied across various sectors:
- Packaging: Companies utilize die cutting for producing custom boxes, inserts, and labels, all tailored to specific products, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics.
- Automotive: In this industry, die-cut components are crucial for creating gaskets, seals, and interior trim elements that require high precision to ensure proper fitting and performance.
- Medical: Precise die cut parts are essential in manufacturing medical devices and disposable items like syringes and bandages where hygiene and accuracy are non-negotiable.
- Electronics: Die cutting is vital for producing insulation materials, gaskets, and protective covers, ensuring reliable performance in electronic devices.
Benefits of Precision Die Cutting
Cost Efficiency in Production
One of the most significant advantages of precision die cutting is its cost efficiency. By streamlining the production process, companies can reduce labor costs and material waste. The ability to produce high volumes of uniform parts quickly means that businesses can benefit from economies of scale, ultimately lowering the cost per unit. Furthermore, the sustainable practices in die cutting, such as material savings, contribute positively to the cost analysis of production.
Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
Precision die cutting offers exceptional accuracy, ensuring that every piece produced meets the specified design. This precision is critical, especially in applications that require tight tolerances. Consistency across batches enhances product reliability, thereby fostering consumer trust. Additionally, advanced technologies allow for real-time adjustments during production, addressing any discrepancies instantly and ensuring that quality standards are upheld.
Versatility in Material Handling
Precision die cutting can handle a wide range of materials, from thin films and fabrics to thicker substrates like rubber and metals. This versatility allows manufacturers to tailor their processes according to the specific needs of their projects. Moreover, the ability to combine different materials in a single cut can lead to innovative product designs, further extending the possibilities of precision die cutting.
Choosing the Right Die Cutting Technique
Flatbed vs. Rotary Die Cutting
Choosing between flatbed and rotary die cutting depends on several factors, including the project requirements:
- Flatbed Die Cutting: Best suited for projects that demand high precision and intricate designs. Ideal for short to medium production runs where a die is required for complex shapes.
- Rotary Die Cutting: Perfect for high-volume production with simpler shapes. This technique offers speed and efficiency, making it a cost-effective option for mass manufacturing.
When to Use Laser Die Cutting
Laser die cutting is an excellent choice for projects that require high precision and flexibility. It is particularly advantageous for creating prototypes, as it does not require the production of a physical die. Additionally, laser cutting can handle complex designs that would be challenging or impossible with conventional cutting methods, making it an attractive option for bespoke projects.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Process
When determining the best die-cutting technique, businesses should consider:
- Material Requirements: Different materials may require different cutting methods; for example, thick materials could benefit from rotary cutting.
- Production Volume: Higher volumes often favor rotary die cutting due to its efficiency, while specialty projects may be better suited for flatbed or laser methods.
- Design Complexity: Complex designs may necessitate the precision offered by laser cutting or flatbed methods.
- Budget and Timelines: Evaluate the overall costs associated with each process alongside the required turnaround time.
Challenges in Precision Die Cutting
Common Issues Faced During Production
Despite the advantages of precision die cutting, several challenges can arise during production. These may include:
- Material Fraying: Edges may fray when cutting certain materials, affecting the quality of the final product.
- Die Wear: Over time, dies can wear down, leading to compromised accuracy and requiring maintenance or replacement.
- Anomalies in Material Thickness: Variability in material thickness can cause inconsistencies in the cutting process.
Error Management and Quality Control
Implementing stringent quality control measures is vital to managing errors in die cutting. Manufacturers can adopt techniques such as:
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping dies sharp and well-maintained prevents wear and tear, ensuring high-quality cuts.
- Automated Quality Checks: Incorporating technology to monitor and adjust processes in real time can address discrepancies swiftly.
- Sample Testing: Conducting sample tests can help identify potential issues before full-scale production.
Staying Up-to-Date with Industry Standards
Adhering to industry standards is crucial in precision die cutting. Regularly reviewing and updating processes to align with technological advancements and regulations ensures compliance and enhances safety. This includes staying informed about new materials and cutting methods that could lead to more efficient and sustainable practices.
The Future of Precision Die Cutting
Emerging Trends in the Industry
The die cutting industry is evolving, with several trends shaping its future:
- Automation: The introduction of automated die cutting systems is streamlining production processes, reducing labor costs, and increasing output quality.
- Sustainable Practices: A growing emphasis on sustainability is pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and reduce waste during the die cutting process.
- Integration with Digital Manufacturing: The convergence of die cutting with digital manufacturing technologies is enabling greater flexibility and customization in production processes.
Innovations in Technology and Materials
Technological innovations, such as advancements in laser cutting and new die materials, are providing manufacturers with enhanced capabilities. For example, the introduction of smart dies equipped with sensors allows for real-time data collection and process optimization. Additionally, the development of new composite materials is expanding the range of applications for precision die cutting.
Preparing Your Business for Future Changes
Preparing for future advancements in precision die cutting requires a proactive approach:
- Invest in Training: Ensuring that staff are well-trained in the latest technologies will improve efficiency and product quality.
- Adapt to Market Changes: Staying responsive to industry trends and client demands will be key to maintaining a competitive advantage.
- Focus on Sustainability: Incorporating sustainable materials and practices will not only meet regulatory requirements but also attract environmentally-conscious consumers.