Understanding AC DC TIG Welders
What is an AC DC TIG Welder?
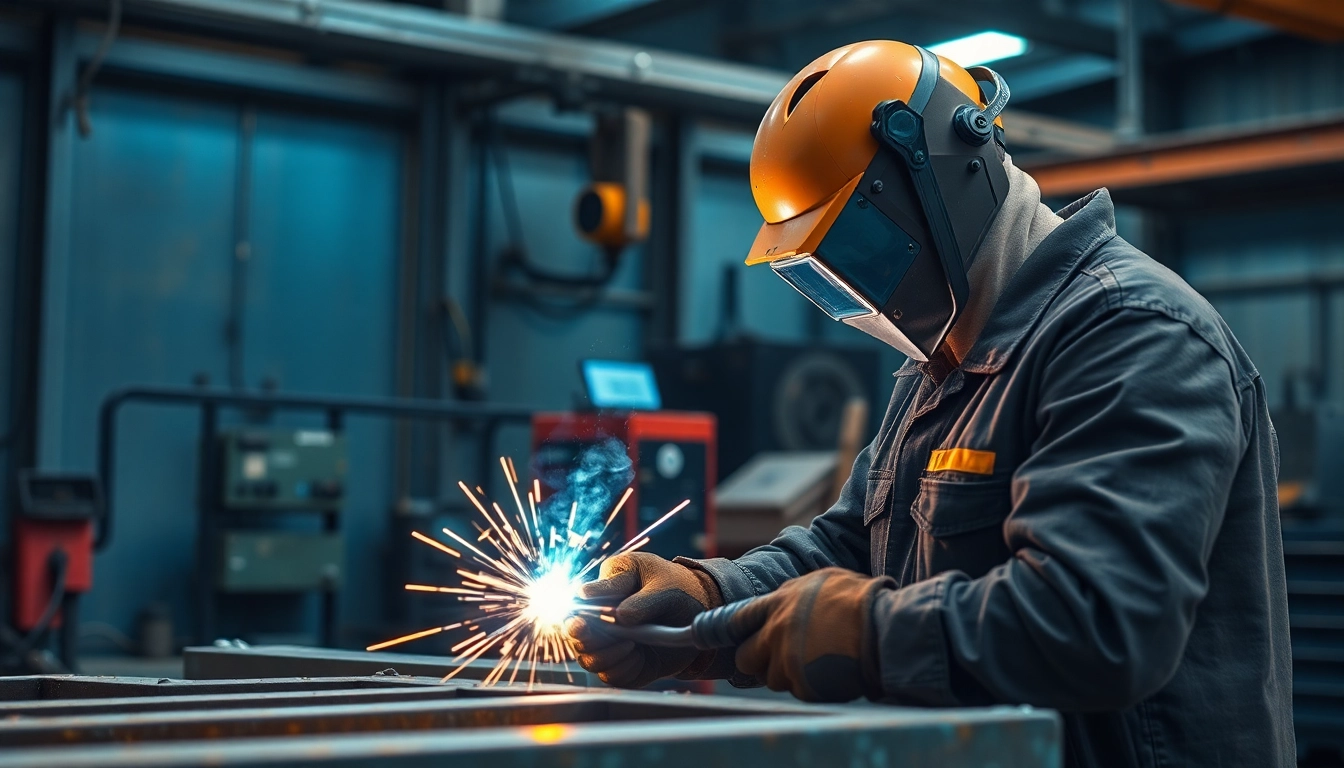
An AC DC TIG welder is a specialized welding machine that allows for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) outputs, making it versatile for a variety of metals and applications. Unlike standard welding machines, AC DC TIG welders can seamlessly switch between these two forms of current, offering precision and control in the welding process. AC is primarily used for welding materials like aluminum, which benefits from this alternating current due to a unique cleaning action that helps remove oxidation. On the other hand, DC is typically employed for welding materials such as steel and copper, which require different electrical characteristics to create a sound weld.
This dual capability not only caters to a wide range of welding applications but also enhances the overall quality of the welds, which is why many professionals (and hobbyists) consider the ac dc tig welder a vital addition to their toolkit.
Key Features of AC DC TIG Welders
- Dual Voltage Capability: The flexibility of using both AC and DC currents allows for a broader scope of applications.
- Precision Control: Many models come equipped with features such as adjustable amperage, pulse welding, and multiple settings that enable high levels of precision.
- Cooling Systems: Proper cooling mechanisms such as fan cooling or water cooling extend the welder’s life and enhance performance during prolonged use.
- Foot Pedal Control: A common feature in AC DC TIG welders, allowing users to manage the welding process hands-free while maintaining precise control over the amperage.
- Interchangeable Electrodes: Users can easily switch tungsten electrodes to suit different materials or types of welds.
- Multiple Modes: Advanced models may come with specialized modes for specific applications like pulse mode for thin materials or spot welding.
Advantages Over Other Welding Types
AC DC TIG welding offers several advantages compared to other welding methods. Firstly, it produces high-quality welds that are often cleaner and require less cleanup afterward, primarily due to the precision control it provides. The ability to weld different materials effectively makes this technique highly versatile. Compared to MIG welding, for instance, TIG welding allows for better control over heat input, thus reducing warping and other heat-related distortions in metals.
Additionally, TIG welding is ideal for projects that require aesthetic concerns, such as architectural piping or artistic metalwork. Finally, while the learning curve might be steep for beginners, the quality of the work produced offers substantial rewards, making it worthwhile in the long run.
Choosing the Right AC DC TIG Welder
Factors to Consider When Buying
When selecting an AC DC TIG welder, several key factors should be considered to ensure you make the right investment for your specific needs:
- Power Output: Assess the amperage range of the welder. A higher amperage allows for thicker materials and more demanding projects.
- Portability: Consider the weight and dimensions of the unit, especially if you plan to move it between job sites or require a space-saving option.
- Duty Cycle: This indicates how long the welder can operate before needing to cool down. A higher duty cycle generally means longer work periods.
- Ease of Use: Look for user-friendly interfaces, clear displays, and intuitive controls, especially for those new to TIG welding.
- Brand Reputation: Choosing a welder from a trusted brand often ensures reliability and consistent performance. Research customer reviews and expert recommendations.
- Available Accessories: Consider what additional accessories (foot pedals, torches, etc.) are included or readily available for purchase.
Top Brands in the Market
Several brands are known for producing high-quality AC DC TIG welders. Some of the top manufacturers include:
- Miller Electric: Known for durability and reliability, Miller offers a range of TIG welders that are well-regarded in the industry.
- Lincoln Electric: Their machines are designed for heavy-duty industrial use and come with innovative features and robust build quality.
- Everlast: A popular choice among hobbyists and professionals alike, known for providing great value for various models.
- PrimeWeld: Offers models that balance performance with affordability, making them good choices for many users.
- Weldpro: Known for their features like high-frequency start and versatility across materials.
Common Misconceptions Addressed
Many misconceptions surround AC DC TIG welding, which can deter potential users from exploring this invaluable technique. Here are a few common myths:
- Only Professionals Can Use TIG Welders: While TIG welding does require practice, many beginner-friendly options are available that make learning accessible.
- TIG Welding is Too Slow: While it can be slower than methods like MIG welding, the quality and precision of the welds often justify the pace.
- AC DC TIG Welders are Expensive: While high-end models can be pricey, many budget-friendly options do not sacrifice quality for cost.
- TIG Welding Cannot be Used for Thick Materials: With the right welder and techniques, TIG can certainly be applied to thicker materials, especially with DC settings.
Applications of AC DC TIG Welding
Industries that Utilize AC DC TIG Welders
AC DC TIG welders find applications across several industries owing to their versatility and precision. Key industries include:
- Aerospace: Used for lightweight structures and high-strength components.
- Automotive: Essential in manufacturing and repair of vehicles, particularly for exhaust systems and chassis components.
- Manufacturing: Commonly used in the production of metal parts, including food and beverage equipment.
- Construction: Used in the installation of critical infrastructure components.
- Artistic Metalworking: Artists utilize TIG welding to create intricate designs and sculptures.
Projects Suitable for AC DC TIG Welding
Various projects are deemed suitable for AC DC TIG welding, particularly those that require precision and cleanliness. These include:
- Fabrication of Stainless Steel Equipment: Ideal for sinks, counters, and storage solutions.
- Aluminum Fabrication: Useful for welding bike frames, aircraft components, and marine applications.
- Metal Art Projects: Artists often choose TIG welding for its ability to create aesthetically pleasing welds.
- Piping Work: Creating pipelines for gas and liquid transportation with minimized contamination risks.
When to Use AC vs DC Settings
Understanding when to use AC or DC settings is critical for achieving optimal results:
- Use AC: For welding aluminum and magnesium, as the AC cycle helps to clean the metal surface during the weld.
- Use DC: For welding materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and non-ferrous metals, as it provides deeper penetration and control.
Best Practices for AC DC TIG Welding
Setting Up Your Workspace
A well-organized workspace is essential for efficient and safe welding. Here are key considerations:
- Lighting: Ensure good visibility by using adequate lighting to enhance focus on welding areas.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper airflow to minimize the inhalation of fumes and gases generated during welding.
- Equipment Arrangement: Keep all tools and materials within reach to maintain workflow.
- Safety Gear: Always wear appropriate safety gear such as welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing.
Welding Techniques for Optimal Results
To achieve the best results with AC DC TIG welding, consider the following techniques:
- Proper Torch Angle: Maintain a 15 to 20-degree angle to achieve effective penetration and bead formation.
- Travel Speed: Adjust your travel speed to maintain consistent puddle control and avoid defects.
- Puddle Control: Learn to manipulate the molten puddle using the tungsten and filler rod effectively.
- Heat Management: Use pulse settings when necessary to control heat-input, especially on thin materials.
Safety Tips and Equipment
Prioritizing safety is crucial in every welding operation:
- Protective Gear: Always wear a properly rated welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing to shield against burns and UV radiation.
- Maintain Equipment: Regularly inspect cables, hoses, and connectors for any signs of wear or damage.
- Emergency Preparedness: Keep a fire extinguisher and first aid kit within easy reach in case of accidents.
- Proper Handling of Gas Cylinders: Ensure cylinders are stored upright and secured in place to avoid tipping.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Routine maintenance will extend the lifespan of your AC DC TIG welder. Here are essential maintenance tasks:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the welder’s exterior, and keep the torch free of contamination and spatter.
- Inspecting Connections: Frequent checks can prevent electrical issues. Look for signs of burn or wear at connectors.
- Cylinder Checks: Inspect gas cylinders for proper pressure and leaks, ensuring they are properly secured.
- Calibration: Schedule periodic checks and calibrations to maintain accuracy in amperage settings.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even experienced welders may encounter issues from time to time. Here are common challenges and their solutions:
- Poor Bead Appearance: May indicate an improper travel speed or temperature setting. Adjust settings and practice bead placement.
- Tungsten Contamination: This can occur when the tungsten contacts the molten metal. Use clean, precise movements to avoid this.
- Inconsistent Arc: Check the settings and connections; ensure the torch and ground clamps are working correctly.
- Excessive Heat Input: Symptoms include warping or burn-through. Reduce amperage settings or increase travel speed.
Upgrading Your AC DC TIG Welder
As your skills progress or project requirements change, the need may arise to upgrade your AC DC TIG welder. Consider these factors:
- Advanced Features: Upgrading may allow access to pulse welding, advanced control interfaces, or automation capabilities.
- Higher Amperage: If you’re working with thicker materials, an upgrade may be necessary for enhanced power needs.
- Increased Portability: If you’re working on-site often, a more portable model with a compact design could facilitate ease of transport.
- Brand Preference: As fidelity to brands evolves, upgrading often means embracing newer technology and improved warranties.